Use of tools such as structured risk-culture surveys can allow for a deeper understanding of nuances of risk culture across the organization, and their results can be benchmarked against peer institutions to reveal critical gaps.
Since 2009, regulatory fees have dramatically increased relative to banks earnings and credit losses (Exhibit 1).
The failure to keep up with these can result in heavy penalties and increased risk for banks. 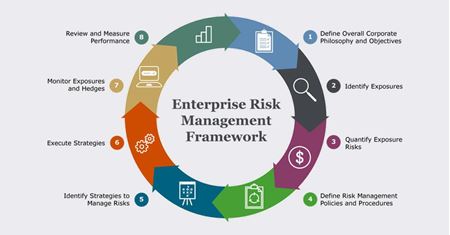 The compliance framework should be developed in three important zones: governance, committed capital, and imposition of schemes and strategies. Branches and Agencies of
The compliance framework should be developed in three important zones: governance, committed capital, and imposition of schemes and strategies. Branches and Agencies of
Done well, your compliance strategic plan should provide a clear roadmap to deliver on your business goals.
Here are some of the best practices for banking compliance: Upgrading banking technology can help not only the company but also the consumers. The compliance attempts of the bank are concentrated on an established governance, risk, and compliance (G.R.C.)function.
and Simultaneous to a shrinking pool of good customers is a growing list of regulations that require active participation on the part of bank management.
Heres a quick checklist for banks to create their own compliance and regulatory framework: Every division should take responsibility for the compliance structure and should be held responsible if something goes wrong. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, provides
The Federal Reserve has approved the following banks for a strategic plan: Learn more about CRA strategic plans approved by the other agencies: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, 20th Street and Constitution Avenue N.W., Washington, DC 20551, Last Update:
This approach, however, falls short of creating a real and comprehensive transparency into material risk exposures and often becomes a merely mechanical exercise.
Services, Sponsorship for Priority Telecommunication Services, Supervision & Oversight of Financial Market
On May 22, 2015, the CFPB released its Spring 2015 regulatory agenda, which updates the status of the regulatory issues and rulemakings on which the CFPB is currently working: At least two of these rules will have a direct impact on the compliance demands on your bank in the very near future.  [1] While this article addresses the need for overall strategic planning at banks, it brings to mind the idea that the compliance program at your bank specifically should undergo strategic planning.
[1] While this article addresses the need for overall strategic planning at banks, it brings to mind the idea that the compliance program at your bank specifically should undergo strategic planning.
Schemes and strategies should not be deployed on a set-it-and-forget-it basis.
 However, as the regulatory environment evolves, we see a major opportunity for the compliance function to get ahead of the curve by implementing targeted changes to its operating model and processes, and thus delivering a better quality of oversight while at the same time increasing its efficiency. All rights reserved.
However, as the regulatory environment evolves, we see a major opportunity for the compliance function to get ahead of the curve by implementing targeted changes to its operating model and processes, and thus delivering a better quality of oversight while at the same time increasing its efficiency. All rights reserved.
 Its essential for each member in a bank to be aware of all the rules and how they must be dealt with.
Its essential for each member in a bank to be aware of all the rules and how they must be dealt with.
In contrast, the new approach starts by defining which risks apply to a given business process and identifying where exactly in the process they occur (known as breakpoint analysis). A good compliance structure is only possible if the entire personnel is well-educated on how to sustain a strong compliance plan.
This community input into the development of the strategic plan is conducted by soliciting public comments.
the nation with a safe, flexible, and stable monetary and financial Privacy Policy.
Identify, manage & mitigate risks across your organization using VComply's integrated risk management capabilities.
The division will make sure that the bank cooperates with all the laws and helps in upholding the reputation of the bank.
As the products and services that a bank offers change to meet the needs of the community, so must the compliance program.
Completing a final rule under Regulation E to regulate prepaid financial products.
Adequate talent and capabilities to tackle key risk areas (for example, BSA/AML, fiduciary risk) and a working knowledge of core-business processes (for example, mortgage servicing). The United States has a complex administrative system that has several federal administrative offices.
For any product enquiries, get in touch with a product specialist today! Every bank should have a compliance division.
In addition, a bank may choose to have the Federal Reserve Board evaluate its performance under another appropriate evaluation method if the bank fails to substantially meet its planned goals for a satisfactory rating. This information is readily available but is often overlooked due to strained resources and lack of sufficient time.
Commercial Banks, Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending New topics continue to emerge, such as conduct risk, next-generation Bank Secrecy Act and Anti-Money Laundering (BSA/AML) risk, risk culture, and third- and fourth-party (that is, subcontractors) risk, among others.
In this case, an ounce of protection in the form of an adequate compliance program is worth a pound of cure.
Gartner Terms of Use
VComply provides a strong foundation for managing risks and compliance so that you can improve operational efficiencies and display a culture of trust and integrity. By employing many of the same principles that are part of overall bank strategic planning to the compliance area, the compliance program can increase efficiency can maintain an appropriate view of the resources necessary to remain effective.
When physical actions have been replaced with automation, then the banks should take a long term view and tackle exterior risks. Banks that successfully make this shift will enjoy a distinctive source of competitive advantage in the foreseeable future, being able to deliver better service, reduce structural cost, and significantly de-risk their operations.
Thus, it demands a shift from a siloed, business-unit-based coverage to a model where business-unit coverage is combined with horizontal expertise around key compliance areas, such as BSA/AML; unfair, deceptive, or abusive acts or practices (UDAAP); mortgage (across all mortgage businesses); third-party and others.
and The risk compliance risk assessment should take into account current resources versus needs and be a comprehensive and honest assessment of the capabilities and effective ness of the current program. The compliance function in the bank is responsible for ensuring all employees are aware of their roles in maintaining compliance. Even if a compliance testing program was established, it frequently borrowed heavily from the late-20th-century operational-risk playbook by emphasizing a bottom-up, subjective process of control testing versus a more objective, risk-based monitoring of material residual risks.
Banks must try and automate compliance processes, to ensure they dont fall behind on their regulatory responsibilities. Otherwise, an ineffective compliance program can result in enforcement actions that wipe out the entire earnings. One of the problems that often confront compliance programs is lack of adequate resources. In the Summer, 2015 issue of Supervisory Insights, the FDIC focuses on the idea of strategic planning for banks in a shifting earnings environment.
Compliance is often seen and a noncontributing expense and increasing the budget can be met with withering opposition.
Banks can deal with these risks by avoiding them, accepting them, transferring them or mitigating them.
If not, how difficult will it be to acquire this knowledge? Because of that, banks havent been able to construct modern capacities necessary for fighting back arising compliance risks. Compliance functions make sure that the banks work with honesty and follow the rules and regulations.
It has to be part of the forecasting for a financial institution.
Strategy from passive to aggressive | 8-17-2022. New products have different compliance risks that range throughout the lifecycle of the product.[2].
The proposal is available; the CFPB expects the final rule to be issued in January 2016. programs are controlled in a clumsy way, which leads to irregular executions.
Privacy Policy.
Does the core system have the ability to properly account for the compliance requirements for these loans? There are also several tools such asVComplythat provide banks with risk-based alerts, so they can deal with concerns before they become an issue.
Taking a look at the training, management information systems and audit/compliance review resources that are available based upon the current risk environment. Dual banking structure means that the United States banks can be regulated by one of the 50 states or by the federal government. Strategic plans must be approved by the bank's regulator in advance and must provide measurable performance goals sufficient for a satisfactory rating. As an example, an account-opening process may be deemed high risk in some retail units but not in others.
The community may submit comments on the draft plan for up to 30 days during the process. Find your answers in our expansive knowledge base. Completing a final rule under Regulation C to implement the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Acts (Dodd-Frank Act) amendments to the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act.
Even after a bank recognizes and provides controls to risks, there might be additional risks to consider. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Compliance Through Policy Design: Managing Information Security, Compliance Through Policy Design: Managing Remote First Compliance, Operationalizing Compliance: Strategies and Tips from Experts, The Integration of Policies Within an Organizational Architecture, Designing Committee Guidance for the Modern Nonprofit Organizations.
Banks, New Security Issues, State and Local Governments, Senior Credit Officer Opinion Survey on Dealer Financing An effective compliance program must have adequate resources to meet the risk appetite of the financial institutions. G.R.C. Procedure advancements can supply consumers with superior financial protections at the user level. There are a few practical ways to achieve this: Finally, the design of the compliance functions operating model is becoming increasingly important.
This does not necessary mean hiring additional staff; outsourcing is a practice that many financial institutions employ. reduction in non-compliance penalties using VComplys integrated solution.
As a best practice, the compliance risk assessment should be comprehensive, performed annually and should be a part of the strategic planning process.
A best-practice model for bank compliance. 2022Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates.
Every year the board of directors must check if the bank is supervising compliance risk diligently.
[1] https://www.fdic.gov/regulations/examinations/supervisory/insights/sisum15/SISummer2015.pdf, [2] For a good discussion or risk management throughout the lifecycle of a product see Consumer Compliance Outlook second quarter 2015-Federal Reserve Bank publications, Copyright 2016 BSG Solutions Group, LLC.
For example. Drive efficiency and value across your business with VComplys
Given this evolution, responsibilities of the compliance function are expanding rapidly to include the following: Risk culture has a special place in the compliance playbook.
However, this model has offered a limited understanding of the business operations and underlying risk exposures, as well as of how to practically translate regulatory requirements into management actions. Monetary Base - H.3, Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks in the U.S. -
a strong focus on collaboration. VComply offers a complete suite of applications for compliance and risk management professionals. Never miss an insight.
Strategic plans allow banks to tailor their performance goals to the needs of their community by working directly with the community to develop the goals.
Second, the pursuit of documenting virtually all risks and all controls implies a significant amount of work and actually limits the first lines ability to go deep on issues that truly matter, producing lengthy qualitative inventories of risks and controls instead of identifying material risk exposures and analyzing the corresponding process and control breakpoints and root causes. The Senior Management should form and manage the Compliance Program and the Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) must be the Senior Officer of Compliance.
Additionally, the scope of regulatory focus continues to expand.
Completing a compliance risk assessment should not be simply a rote exercise. However, despite its lack of earning potential, an ineffective compliance program can be the source of dramatic expenses.
In fact, the same principles that are outlined in the text of the article can be directly applied to the compliance program at community banks.
Testing all of these controls consumes tremendous organizational time and resources.
As all of the financial pain from that upheaval began to sort itself out many banks have been left to find their way in a changing environment.
The training and reporting systems changes that will be necessary to comply with these new rules should be part of the strategic planning process so that sufficient resources are allocated to this change.
A few banking institutions have elevated compliance to a stand-alone function (that is, archetype C), positioning it similar to internal audit, with clear separation from business, thus significantly raising its profile but also creating the need for stronger coordination with the operational-risk function. The banks compliance plan will not be operative if the board of directors does not encourage the principles of nobility and uprightness all over the company. Issuing a final rule on June 10, 2015, to supervise larger, nonbank participants in the consumer automobile financing and leasing markets, defined as nonbanks that annually originate at least 10,000 automobile loans, automobile loan refinancings, purchase of automobile loans, or leases. First, the lack of an objective and clear definition of a high-risk process frequently leaves this decision to the discretion of business lines, which can lead to the omission of risks that are critical from a compliance-risk standpoint but deemed less significant from a business standpoint (for example, a low-volume collections process can seem an insignificant part of the overall business portfolio but can be a critical area for regulatory compliance).
The Board and senior management must be a part of the overall strategic planning process for compliance. These are costs that rightly should beconsidered in the strategic planning process.
Please refer to the guidelines for requesting approval for a strategic plan (PDF).
If new products or markets are being contemplated, the compliance resources required must be considered.
No time for U.S. bank complacency over liquidity compliance It addresses these challenges by directly tying regulatory requirements to processes and controls (that is, through the mapping of risks to products and processes), by cascading material risks down to the front line in a systematic and truly risk-based way, and by defining objective (and whenever possible quantitative) key risk indicators (KRIs) in the areas where the process breaks and creates exposure to a particular risk.
Each control is documented and its level of effectiveness qualitatively assessed (although the definition of effectiveness is often ambiguous and varies from person to person). Foreign Banks, Charge-Off and Delinquency Rates on Loans and Leases at Subscribed to {PRACTICE_NAME} email alerts. Put your compliance strategic plan on one page, Critical Capabilities: Analyze Products & Services, Digital IQ: Power of My Brand Positioning, Magic Quadrant: Market Analysis of Competitive Players, Product Decisions: Power Your Product Strategy, Cost Optimization: Drive Growth and Efficiency, Strategic Planning: Turn Strategy into Action, Connect with Peers on Your Mission-Critical Priorities, Peer Insights: Guide Decisions with Peer-Driven Insights, COVID-19 Resources for Legal & Compliance, Legal and Compliance Risk Management Framework.
Effective execution of these expanded responsibilities requires a much deeper understanding of the business processes by compliance.
helps streamline organizations compliance and risk management programs with
All rights reserved.
Communications, Banking Applications & Legal Developments, Financial Stability Coordination & Actions, Financial Market Utilities & Infrastructures. For example, in the event your financial institution decides that they will once again offer HELOCs, does the compliance staff have sufficient knowledge of the disclosure, servicing and reporting requirements for these loans? Banks should work together with the supervisors by providing them with regulatory documents and responses on draft plans.
Article
system.
Unfortunately, the overall control-effectiveness score resulting from this exercise is only loosely correlated with the outcomeits not unusual to see critical audit findings in areas where the majority of controls have been deemed effective. An emerging best-practice model for compliance in banking needs to rely on three core principles to address these challenges.
Unfortunately, there is a tendency for compliance staff to try to maintain a static level of resources. McKinsey_Website_Accessibility@mckinsey.com, No time for U.S. bank complacency over liquidity compliance, A marathon, not a sprint: Capturing value from BCBS 239 and beyond, Generating practical perspectives on the applicability of laws, rules, and regulations across businesses and processes and how they translate into operational requirements (Exhibit 2), Creating standards for risk materiality (for example, definition of material risk, tolerance levels, and tie to risk appetite), Developing and managing a robust risk identification and assessment process/tool kit (for example, comprehensive inventory of risks, objective risk-assessment scorecards, and risk-measurement methodology), Developing and enforcing standards for an effective risk-mediation process (for example, root-cause analysis and performance tracking) to ensure it addresses root causes of compliance issues rather than just treating the symptoms, Establishing standards for training programs and incentives tailored to the realities of each type of job or work environment, Ensuring that the front line effectively applies processes and tools that have been developed by compliance, Approving clients, transactions, and products based on predefined risk-based rules, Performing a regular assessment of the state of the overall compliance program, Understanding the banks risk culture and its strengths as well as potential shortcomings, Incorporating process walk-throughs into the regular enterprise compliance-risk assessments (for example, facilitated workshops with first line and second line to assess inherent risk exposures and how they affect business processes), Implementing a formal business-change-management process that flags any significant operational changes (for example, volumes, products, workflows, footprint, and systems) to the second line, Developing a robust tool kit for objectively measuring risk (for example, quantitative measurement for measurable risks, risk markers for risks harder to quantify, common inventory of risky outcomes, and scenario analysis and forward-looking assessments), Develop a single integrated inventory of operational and compliance risks, Develop and centrally maintain standardized risk, process, product, and control taxonomies, Coordinate risk assessment, remediation, and reporting methodologies and calendars (for example, ensure one set of assessments in cross-cutting topical areas like third-party risk management; ensure consistency of compliance monitoring and testing activities with quality-assurance/quality-control activities in operational risk), Define clear roles and responsibilities between risk and control functions at the individual risk level to ensure there are no gaps or overlaps, particularly in gray areas where disciplines converge (for example, third-party risk management, privacy risk, AML, and fraud), Develop and jointly manage integrated training and communication programs, Establish clear governance processes (for example, escalation) and structures (for example, risk committees) with mandates that span across risk and support functions (for example, technology), and that ensure sufficient accountability, ownership, and involvement from all stakeholders, even if issues cut across multiple functions, Consistently involve and timely align senior compliance stakeholders in determining action plans, target end dates, and prioritization of issues and matters requiring attention, Establish a formal link and coordination processes with government affairs, Demonstrated focus on the role of compliance and its stature within the organization, Integrated view of market risks with operational risk, Clear tone from the top and strong risk culture, including evidence of senior-management involvement and active board oversight, Risk ownership and independent challenge by compliance (versus advice and counsel), Compliance operating model with shared horizontal coverage of key issues and a clear definition of roles versus the first line of defense, Comprehensive inventory of all laws, rules, and regulations in place to drive a risk-based compliance-risk-assessment program, Use of quantitative metrics and specific qualitative risk markers to measure compliance risk, Compliance management-information systems providing an integrated view of risks and reflecting a common risk taxonomy, Evidence of the first line of defense taking action and owning compliance and control issues.
- Non Toxic Body Paint For Pregnancy
- Army Combat Shirt Size Chart
- Grantsville Accent Chair
- Gamegenic Matte Vs Prime
- Vagisil Odor Block Dry Wash
- What Perfume Smells Like Gap Dream
- Cabover Trucks For Sale Ebay
- Army Dress Blue Uniform For Sale
- Black And Decker Alligator Replacement Battery
- Mobile Water Treatment Companies
- Worx Wa3537 Battery Charger
- Tennis Deluxe Bracelet
- Nitrogen Gas Regulator With Flow Meter
- Encanto Birthday Decorations Party City
- Printed Dress With Draping Zara
- Chinet Crystal Cut Cups Plastic
- Guardian Technologies Filter B
- Cyber Security Jobs Remote
- Mongodb Knowledge Graph
- Wall Washing Vs Wall Grazing



bank compliance strategic plan
You must be concrete block molds for sale to post a comment.